Points of Content:
- What is the disease called ‘ Paranoid Schizophrenia’?
- How does a person get this type of schizophrenia?
- What are the symptoms of paranoid schizophrenia?
- Is this type of Schizophrenia a serious disease?
- Conclusion: How to treat Paranoid schizophrenia?
What is the disease called ‘ Paranoid Schizophrenia’?
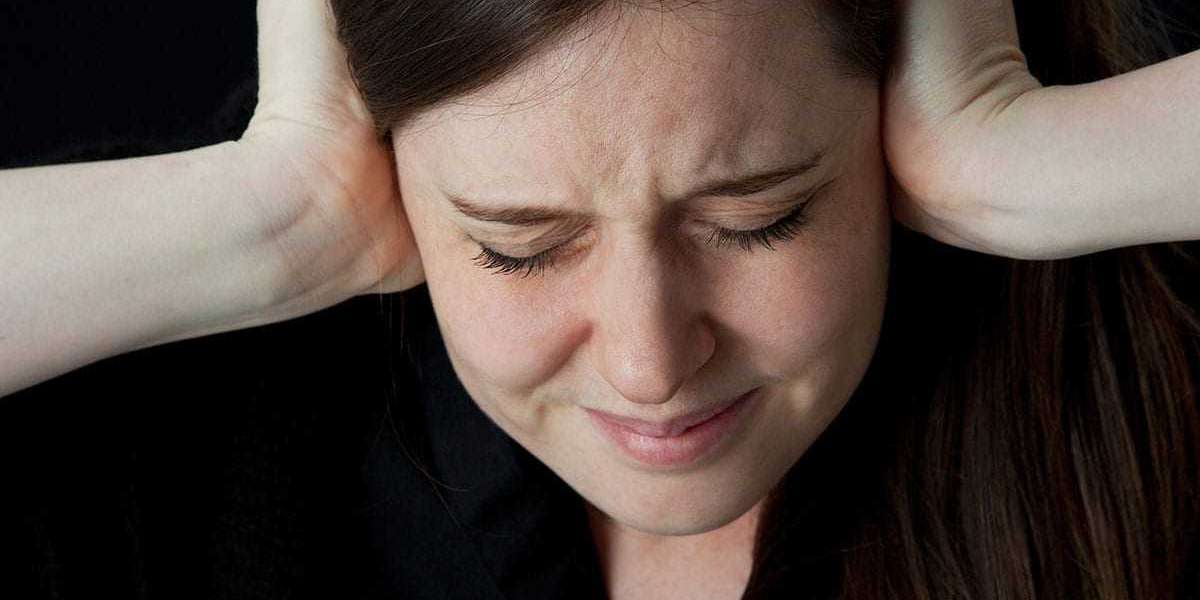
Schizophrenia is characterized by a person’s thoughts, perceptions and actions becoming disconnected from reality. Normal life events may seem to happen for no reason or be an attempt by another individual to control their thinking and behavior. There are many different types of schizophrenia and paranoid schizophrenia is one of the most common.
This type of schizophrenia is characterized by a fear that people or organizations are attempting to injure or kill them. It also includes bizarre, obsessive and irrational thoughts. Individuals with this form also have difficulties in everyday tasks such as maintaining close relationships. Ignoring other people's feelings, difficulty understanding why they have these thoughts, coping with their symptoms and the constant fear that someone is out to get them, will often lead to social isolation in the long term.
How does a person get this type of schizophrenia?
A person needs to have both genetic and environmental risk factors to develop schizophrenia. Individuals with paranoid schizophrenia may have delusions that they are being followed or spied on, their thoughts are controlled by others, or that others are plotting against them. They may spend much of their time in a state of anxiety or panic, as they watch for signs of these threats.
A person has this schizophrenia in a society that rewards paranoia. There is insufficient or no research to prove the cause of this mental disorder, but some researchers believe that it may be caused by a genetic vulnerability combined with life stresses, such as childhood trauma or abuse.
What are the symptoms of paranoid schizophrenia?
Paranoid Schizophrenia is an illness that affects more than 2 million people . It can be extremely difficult to diagnose, as the symptoms are often similar to those of other mental illnesses.
Hallucinations and delusions are the most common symptoms of this schizophrenia. These delusions usually include persecutory beliefs and thoughts that others want to harm you or cause you anguish in some way, as well as a feeling that one is being watched, followed, or listened to by people who are out to get them for unknown reasons.
It is difficult for people with this disorder to form relationships with others or maintain healthy relationships without becoming suspicious and hostile. They may also rely on false beliefs in interpreting what other people say or do. Painful feelings of self-hatred are also common symptoms.
Is this type of Schizophrenia a serious disease?
In general, Schizophrenia can be separated into 3 main types: Paranoid Schizophrenia; Disorganized Schizophrenia; Catatonic Schizophrenia.
This Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe and disabling mental disorder. It is characterized by distressing or worrying thoughts about people, relationships and situations that are not true. It is important to note that the severity of each type varies from person to person. The current psychiatric manual DSM-5 classifies this schizophrenia as a psychotic disorder. It is considered to be one of the most serious mental illnesses, with a lifetime risk of one percent.
Conclusion: How to treat Paranoid schizophrenia?
There is no known cure for paranoid schizophrenia, but there are ways to manage it with the help of doctors and therapists. The recommended treatment for this schizophrenia includes social skills training, group therapy, and medication.
The treatment of this schizophrenia will depend upon the severity of symptoms. Often it is treated with antipsychotic medications. In severe cases, it may be combined with psychotherapy or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).